When building web applications with React, you'll often come across the terms "controlled" and "uncontrolled" components. These terms refer to how React manages form elements like input, textarea, and select. Understanding the difference between controlled and uncontrolled components is crucial for efficient development and managing state effectively.

So, React offers two ways to manage form elements: controlled components and uncontrolled components. Choosing the right approach can make a big difference in your application's functionality and maintainability. Let's dive in and understand the key differences between these two beasts!
Controlled Components: Keeping a Tight Grip
In React, controlled components are those where form data is controlled by React. This means that React state holds the value of the form element. Whenever the user interacts with the form element, React updates the state to reflect the change.
Theory:
Controlled components give you more control over the form data. Since the form data is stored in React state, you can easily manipulate and validate it. You can also synchronize multiple form elements, making it easier to implement features like form validation or dynamic form behavior.
Imagine a text input field where you want to track every keystroke the user makes. In controlled components, React's state acts as the single source of truth for the form data. Here's how it works:
State Management: You define a state variable in your React component to hold the current value of the form element.
Controlled Input: The
valueattribute of the form element (like an<input>) is set to the state variable. This binds the input to the state.Event Handlers: When the user interacts with the form element (e.g., typing), you define an event handler function.
Update State: Inside the event handler, you update the state variable using
setStatewith the new value from the form element.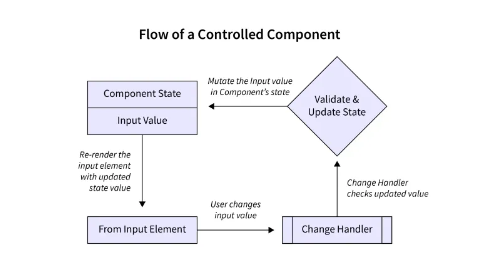
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function ControlledInput() {
const [inputText, setInputText] = useState('');
const handleChange = (event) => {
setInputText(event.target.value);
}
return (
<div>
<label>Name:</label>
<input type="text" value={inputText} onChange={handleChange} />
<p>You entered: {inputText}</p>
</div>
);
}
In this example, the inputText state variable holds the current value of the input field. Whenever the user types, the handleChange function updates the state, keeping React and the displayed value in sync.
Benefits of Controlled Components:
Predictable Behavior: Since React manages the state, you have more control over validation, error handling, and conditional rendering based on form data.
Easy Data Flow: Data flows from child components (inputs) to parent components (state management) for better organization.
Uncontrolled Components: Loosening the Reins
Uncontrolled components, on the other hand, allow the DOM to control the form data. In uncontrolled components, the form data is managed by the DOM itself. React still provides a way to access this data, but it doesn't control it directly.
Theory:
Uncontrolled components are useful when you need to integrate with non-React code or manage form data without maintaining state in React. They can also be beneficial for performance optimization in certain scenarios.
Uncontrolled components take a different approach. They don't rely on React's state for form data. Instead, the form element itself holds the current value.
Refs: You use the
useRefhook to create a reference object that points directly to the DOM element (the input field).DOM Access: To access the current value, you use the
current.valueproperty of the ref object.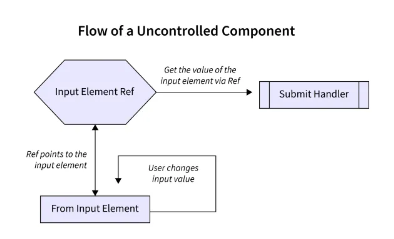
import React, { useRef } from 'react';
function UncontrolledInput() {
const inputRef = useRef(null);
const handleClick = () => {
console.log(inputRef.current.value);
}
return (
<div>
<label>Name:</label>
<input type="text" ref={inputRef} />
<button onClick={handleClick}>Get Value</button>
</div>
);
}
Here, the inputRef ref object points to the input element. The handleClick function retrieves the current value directly from the DOM using inputRef.current.value.
Benefits of Uncontrolled Components:
Simpler for Simple Forms: For quick forms with minimal data manipulation, uncontrolled components can be easier to set up.
Third-Party Libraries: Some third-party libraries might work better with uncontrolled components.
Choosing the Right Weapon
While both approaches have their merits, controlled components are generally recommended for most React applications. They offer better control, easier debugging, and improved maintainability, especially for complex forms. Uncontrolled components can be a good choice for simple forms or integrating with third-party libraries.
Remember:
Controlled components require more code for state management but offer better control.
Uncontrolled components can be simpler for basic forms but might be trickier to manage in complex scenarios.
By understanding these concepts, you'll be well-equipped to choose the right approach for your React form components, leading to cleaner, more manageable applications.
Conclusion
In summary, controlled components are managed by React state, providing more control and synchronization, while uncontrolled components delegate control to the DOM, offering flexibility and performance benefits in certain scenarios. Choosing between controlled and uncontrolled components depends on the specific requirements of your application and the level of control you need over form data. Both approaches have their advantages and use cases, so it's essential to understand them thoroughly to make informed decisions while developing React applications.

To read more about tech, web development & open source, you can follow me on Hashnode and Twitter (@MadhuSaini22) and If this blog helped you in any way then you can sponsor my work and show love and support.
Thank you so much for reading! 👩💻
